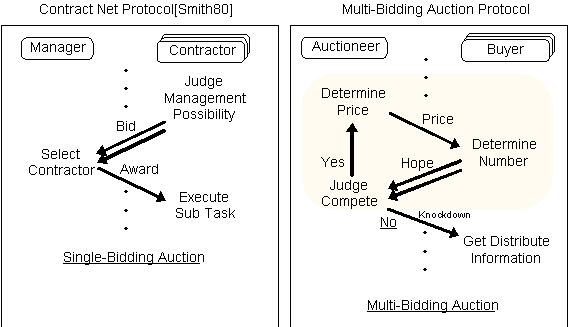
As an interaction protocol for
agent-agent communication, the Contract Net Protocol is well known.
This protocol is for a Single-Bidding auction in which each contractor
makes a bid only once, as shown in Fig.1. We propose a Multi-Bidding
Auction Protocol for agent-agent communication.

Auction characteristics of two different types are shown in Table 1. The Multi-Bidding Auction has several merits compared with the Single-Bidding Auction.
There are some difficulties to
realize an electronic Multi-Bidding Auction, as shown in Fig.2.
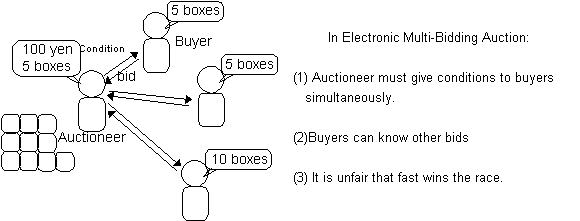
Our protocol is based on following approaches:
(1)Impartiality
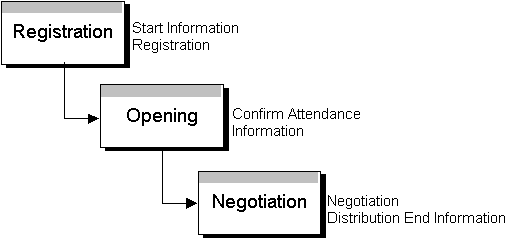
Multi-bidding Auction Protocol
has two types of agents: an auctioneer agent and buyer agents,
and has three stages of protocols, as shown in Fig.3. The first
stage is "Registration". The auctioneer agent makes
and delivers Start Information of an auction, for example using
e-mail or web-pages. The auctioneer agent gathers buyer agents
and registers them to the auction. The second stage is "Opening".
The auctioneer agent confirms buyer agents attendance and starts
the auction. The third stage is "Negotiation". The auctioneer
agent determines goods price and sends buyer agents this price.
Buyer agents determine the number of goods that they wants to
buy at the price. The auctioneer agent determines the number and
the agents who get the goods.
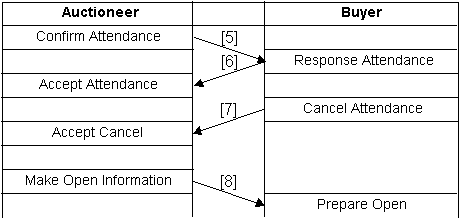
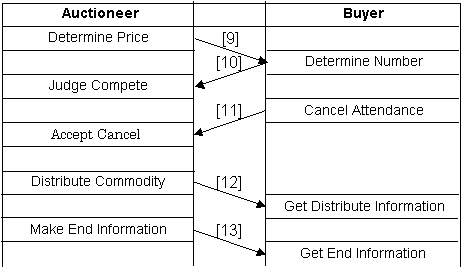
The proposed protocol is shown
in Fig.4.
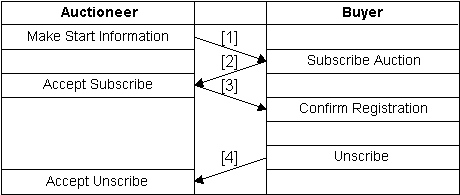
Message examples in the protocol
is shown in Fig.5.


We demonstrate an auction for Flower market.
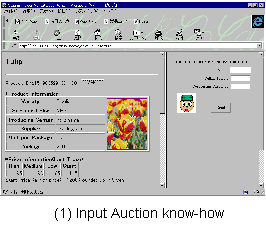
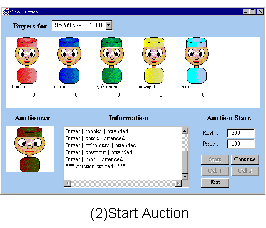
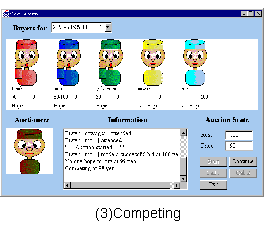
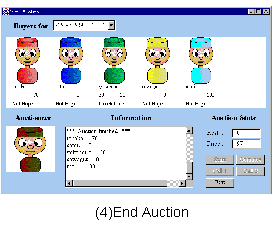
The protocol realizes:
(1) Impartiality
(2) Distribution Logic
(3) Free and Flexible
The protocol can be used in many fields for example:
(1) Real Auction -> Buying at an auction [Varian,95]
(2) Personal Travel Assistance -> Buying a ticket
(3) Network Provisioning and Management
-> Setting up a stream
[Smith 80] R.Smith, The Contract Net
Protocol: High Level Communication and Control in a Distributed
Problem Solving, IEEE Trans. Comps.29(12), pp.1104-1113
[Varian 95] Hal R. Varian, Economic Mechanism Design for Computerized Agents: First USENIX Workshop on Electronic Commerce July 11-12, 1995 pp13-21