| FIPA | 96/06/13 18:22 |
| FOUNDATION FOR INTELLIGENT PHYSICAL AGENTS | nyws027 |
| Source: R. Zarnekow, A. Meyer, H. Wittig (Multimedia Software GmbH) |
Agent Standardization Issues in Electronic Commerce Systems
Position Paper
1. Motivation
With the increasing importance of electronic commerce across the Internet the need for agents
to support both consumers and providers in purchasing and selling goods is growing rapidly.
A number of prototypes have been developed to simulate an agent-based virtual marketplace
(MAGMA, Kasbah, GroupLens).
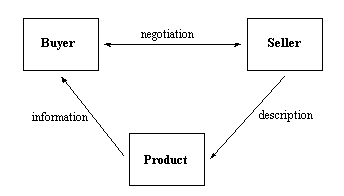
As shown in Fig. 1 the traditional approach to electronic commerce requires a direct
communication between the potential buyer and seller. The buyer collects information about a
product by directly accessing the information provided by the seller. If the offer satisfies his
needs he negotiates directly with the seller of the product. Negotiation, delivery and payment
are usually done manually.

Figure 1
2. Architecture and Interfaces
The traditional approach has the following disadvantages:
An agent-based architecture for electronic commerce allows the creation of a virtual
marketplace in which a number of autonomous or semi-autonomous agents trade goods. This
approach offers a number of new opportunities to reduce or even eliminate the disadvantages
mentioned above. Agents are able to examine a large number of products before making a
decision to buy or sell. This not only eliminates the need to manually collect information about
products but also allows to negotiate an optimal price with the various sellers of a good.
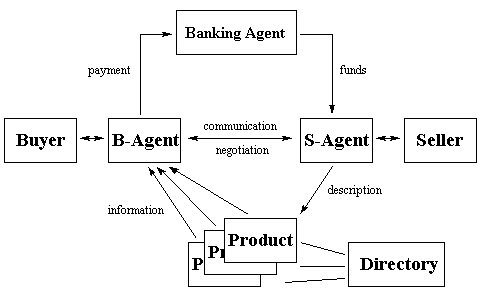
Figure 2: Agent-based architecture
Fig. 2 shows the general architecture of an agent-based virtual marketplace. Instead of buyers
and sellers, buying- and selling-agents communicate and negotiate with each other. The
buying-agent collects information about a number of products and presents its conclusions to
the buyer. The architecture must support some kind of type management or classification trees
in which all goods are integrated. If the buyer is interested in purchasing the product the
buying-agent contacts the selling agent and starts the negotiating process. During negotiations
the agents are able to react to new feedback and go back to collect information about
different products or services. Payment issues are settled automatically over an electronic
banking facility.
3. Issues for Standardization
In order to implement the described system, a number of interfaces have to be specified and
standardized. In the context of FIPA, the following interfaces are of particular importance:
For other interfaces existing standards can be used. These interfaces include:
4. Related Work
OMG: Trader, Collections, Startup Services RFP (OS RFP5)
W3C and CommerceNet Joint Electronic Payment Initiative
5. Literature:
Tsvetovatyy / Gini: Toward a virtual marketplace
Chavez / Maes: Kasbah: An agent marketplace for buying and selling goods
Resnick: The role of brokers in electronic commerce
Vogel / Wittig: Discovering Mobile Code
Authors:
Ruediger Zarnekow, Andy Meyer, Hartmut Wittig
Multimedia Software GmbH Dresden
Business Unit Intelligent Agents and Systems
Riesaer Str. 5, 01129 Dresden, Germany
Tel.: +49 351 8505 354
e-mail: ruediger.zarnekow@mms-dresden.telekom.de
http://www.dtag.de/mms-dresden